Understanding Prenatal Care
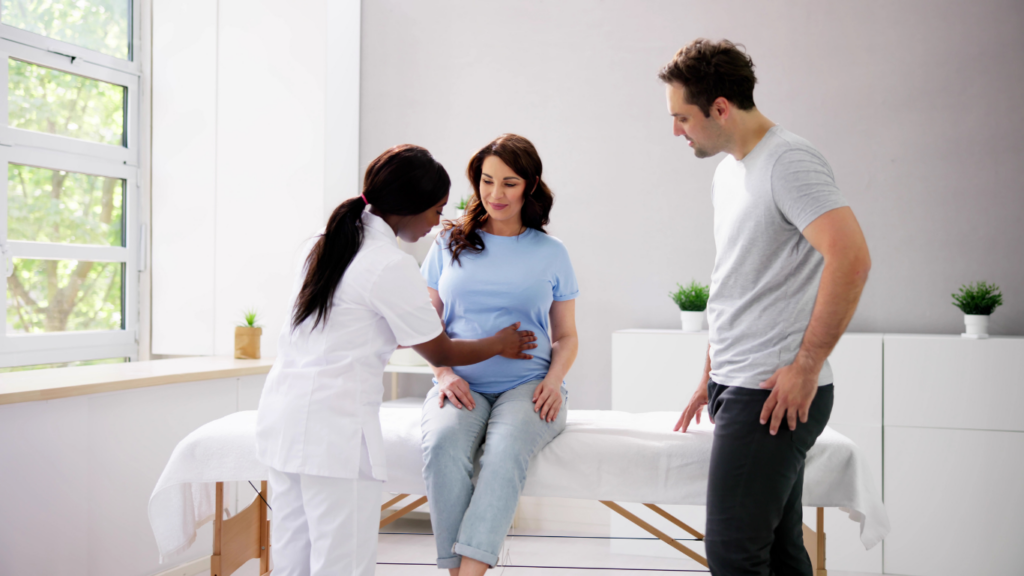
Prenatal care involves regular medical checkups and assessments that monitor the health of both mother and baby. Early and consistent prenatal visits help detect and prevent potential complications. Examples of key prenatal assessments include blood tests, ultrasounds, and monitoring fetal heart rate.
I found that each trimester has distinctive milestones that guide the prenatal care schedule. In the first trimester, initial visits typically involve comprehensive health evaluations and nutritional guidance. Examples of these evaluations include blood tests for anemia and infections, genetic screening, and calculating the due date.
During the second trimester, prenatal visits often focus on tracking the baby’s growth and screening for any developmental abnormalities. Routine ultrasounds are performed during this stage to check the baby’s anatomy and the placenta’s position. I noticed how these screenings provide invaluable insights into my baby’s health and development.
The third trimester concentrates on preparing for labor and delivery. These visits often include monitoring the baby’s position, checking the cervix for dilation, and screening for gestational diabetes. Assessments like group B strep tests also help ensure I’m ready for a safe delivery.
Understanding prenatal care has enhanced my confidence throughout my pregnancy journey, providing me with the knowledge to ensure both my baby’s and my well-being.
Key Milestones in Prenatal Care
Understanding the key milestones in prenatal care helps ensure both a healthy mother and baby. I’ll break down the important milestones by trimester.
First Trimester
In the first trimester, initial visits focus on confirming the pregnancy and estimating the due date. Regular prenatal checkups include:
- Health Assessments: Doctors conduct blood tests, urine tests, and initial ultrasounds to evaluate overall health and detect potential complications.
- Nutritional Guidance: Guidance on prenatal vitamins, folic acid, and diet helps support the baby’s development.
- Screening Tests: Tests like nuchal translucency screening assess the risk of chromosomal conditions.
Second Trimester
The second trimester involves monitoring the baby’s growth and health closely. Key milestones include:
- Anatomy Scan: Around 18-22 weeks, an ultrasound examines the baby’s organs and measures growth.
- Glucose Screening: A glucose tolerance test around 24-28 weeks checks for gestational diabetes.
- Fetal Movement: By week 20, mothers usually feel the baby’s movements, indicating healthy development.
Third Trimester
- Position Monitoring: Regular checkups monitor the baby’s position, essential for planning the delivery method.
- Group B Strep Test: Performed around week 36, this test screens for Group B Streptococcus to prevent infection.
- Labor Preparation: Discussions about labor signs, pain management, and delivery preferences ensure readiness for birth.
Essential Prenatal Checkups

Regular prenatal checkups offer a structured way to ensure the health of both the mother and the baby. Specific checkups and milestones are critical to monitor throughout the pregnancy.
Routine Examinations
Routine examinations start as soon as pregnancy is confirmed. These include checking blood pressure, weight, and urine. Blood pressure monitoring detects hypertension, which can lead to complications. Weight checks ensure healthy weight gain. Urine tests screen for gestational diabetes and urinary tract infections. These exams typically occur monthly in the first two trimesters and then bi-weekly or weekly in the third trimester. During these visits, fetal growth is also measured, often using a tape measure from the top of the pubic bone to the top of the uterus. Listening to the baby’s heartbeat with a Doppler device reassures both the healthcare professional and the expectant mother.
Specialized Screenings
Specialized screenings are essential to detect potential issues that routine exams might miss. In the first trimester, an ultrasound is used to confirm the due date and check for multiple pregnancies. A blood test checks for chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome. In the second trimester, an anatomy scan at around 20 weeks examines the baby’s organs, spine, and limbs, checking for developmental abnormalities. A glucose tolerance test screens for gestational diabetes. In the third trimester, a Group B Streptococcus (GBS) test involves collecting a sample from the vagina and rectum to check for GBS bacteria, which could harm the baby during delivery. If complications arise, additional ultrasounds or non-stress tests may be necessary.
By understanding the importance of these routine and specialized checkups, I feel equipped to ensure my health and my baby’s well-being throughout pregnancy.
Benefits of Prenatal Care
Prenatal care offers numerous advantages that ensure the well-being of both mother and baby during pregnancy. It’s essential for monitoring health and preventing complications through timely interventions.
Health Benefits for Mother
Regular prenatal care has numerous health benefits for the mother. Routine checkups help detect conditions like gestational diabetes and preeclampsia early. Early detection enables prompt treatment and management. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, weight, and urine ensures any abnormalities are addressed swiftly. Nutritional guidance provided during prenatal visits helps maintain a balanced diet, essential for both the mother’s and baby’s health. Furthermore, personalized healthcare advice helps manage pregnancy-related discomforts such as morning sickness, back pain, and fatigue. Overall, prenatal care reduces the risk of complications and promotes a healthier pregnancy.
Health Benefits for Baby
Prenatal care is crucial in safeguarding the baby’s health. Through regular ultrasounds and screenings, healthcare providers monitor the baby’s growth and development. Early identification of congenital anomalies paves the way for timely interventions. Appropriate management of maternal health conditions, such as high blood pressure or diabetes, prevents adverse effects on the baby. Nutritional guidance ensures the mother consumes essential nutrients, supporting the baby’s development. Regular checkups also monitor the baby’s heart rate and movements, ensuring they remain within healthy ranges. Early detection and management of potential issues during prenatal visits enhance the likelihood of a safe delivery and robust newborn health.
Challenges and Solutions
Prenatal care is essential, but it’s not without challenges. Many expecting mothers face obstacles that can hinder their ability to receive proper care.
Common Obstacles
Several obstacles can interfere with prenatal care.
- Financial Constraints: The cost of prenatal visits, tests, and treatments can be high. For example, ultrasounds and specialized screenings may require significant out-of-pocket expenses.
- Lack of Access: Many women live in areas with limited access to healthcare providers. Rural areas often lack specialized prenatal services.
- Work Commitments: Pregnant women with demanding jobs may find it difficult to attend regular checkups. Appointments may conflict with work schedules.
- Transportation Issues: Reliable transportation is not always available. This can be especially problematic in areas without public transit.
- Health Literacy: Understanding medical terms and instructions can be challenging. This may lead to miscommunication and missed appointments.
Strategies for Overcoming Barriers
Addressing these barriers requires practical strategies.
- Financial Assistance: Look for insurance programs and financial aid specifically for prenatal care. Organizations like Medicaid and community health centers often provide support.
- Local Resources: Use local and online resources to find nearby prenatal services. Telehealth options can bridge gaps in areas with limited access.
- Flexible Scheduling: Talk to employers about adjusting work hours. Many companies offer flexible schedules for prenatal appointments.
- Transportation Solutions: Utilize ride-sharing services or community programs designed to assist pregnant women. Some hospitals offer transportation services for patients.
- Education and Communication: Seek clear explanations from healthcare providers. Use reliable sources like CDC and WHO to understand prenatal care requirements.
Overcoming these challenges ensures a healthier pregnancy journey. These strategies help access essential prenatal care, promoting well-being for both mother and baby.